Understanding Cancer: Types, Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Treatments

Cancer, one of the most dangerous diseases in the world, continues to be a significant global health concern. It affects millions of people annually, causing immense physical, emotional, and economic burden. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can play a crucial role in fighting against this devastating illness.
Cancer continues to present a formidable challenge, but with increased awareness, early detection, and advancements in treatment options, the outlook is progressively improving. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of cancer. Furthermore, supporting ongoing research, promoting preventive measures, and embracing innovative therapies contribute to a future where cancer is no longer a life-threatening disease. Remember, early detection and timely intervention remain pivotal in the fight against cancer.
Contents
Types of Cancer in detail:
- Breast Cancer: Breast cancer develops in the breast tissue and primarily affects women, but men can also be affected. Risk factors include age, family history, genetic mutations (such as BRCA1 and BRCA2), hormonal factors, and lifestyle choices. Common symptoms include a lump or thickening in the breast or underarm, changes in breast size or shape, nipple discharge, and breast pain. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and hormone therapy.

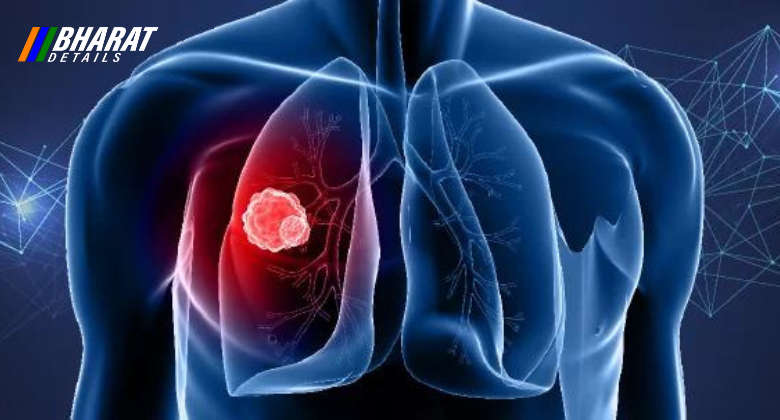
- Lung Cancer: Lung cancer originates in the lungs and is often associated with smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke, radon, asbestos, or other carcinogens. Symptoms may include a persistent cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing up blood, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. Treatment options depend on the type and stage of lung cancer but may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
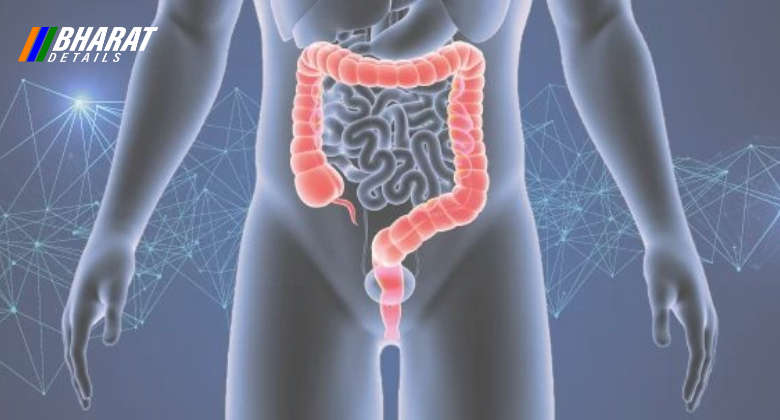
- Colorectal Cancer: Colorectal cancer affects the colon or rectum and usually develops from polyps or abnormal growths in the inner lining. Risk factors include age, family history, inflammatory bowel disease, certain genetic syndromes, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and a diet high in processed meats and low in fiber. Symptoms can include changes in bowel habits, rectal bleeding, abdominal discomfort, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
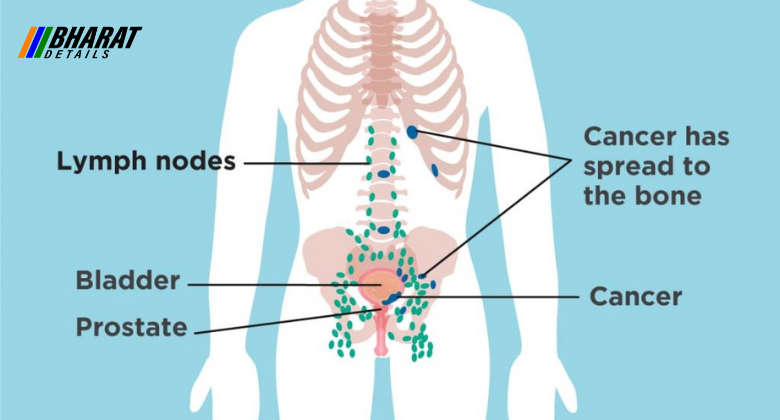
- Prostate Cancer: Prostate cancer develops in the prostate gland and is more common in older men. Risk factors include age, family history, race, obesity, and certain genetic mutations. Symptoms may include urinary problems (such as frequent urination, weak urine flow, or blood in the urine), erectile dysfunction, pain in the hips or lower back, and unexplained weight loss. Treatment options for prostate cancer include active surveillance, surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.
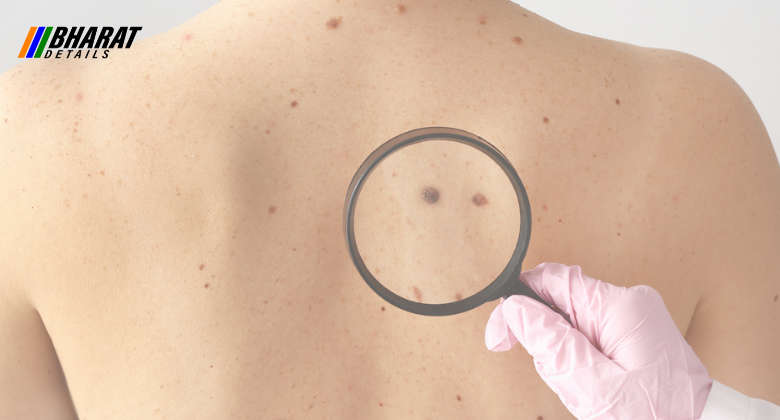
- Skin Cancer: Skin cancer occurs when skin cells undergo abnormal growth due to damage from ultraviolet (UV) radiation, typically from the sun or tanning beds. The three main types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Risk factors include excessive sun exposure, fair skin, history of sunburns, family history, and a weakened immune system. Symptoms can include new or changing moles, non-healing sores, or abnormal skin growths. Treatment options depend on the type and stage of skin cancer but may involve surgery, radiation therapy, topical medications, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy.
- Leukemia Cancer: Leukemia is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow, resulting in the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells. There are different types of leukemia, including acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Risk factors vary depending on the type of leukemia but can include genetic factors, exposure to certain chemicals, radiation, and certain genetic disorders. Symptoms may include fatigue, frequent infections, unexplained weight loss, easy bruising or bleeding, and bone or joint pain. Treatment options include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and stem cell transplant.
Each cancer type has its unique characteristics, risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options. By increasing awareness and knowledge, individuals can actively participate in early detection, prevention strategies, and personalized treatment plans. Remember, regular screenings, healthy lifestyle choices, and prompt medical attention play a crucial role in combating cancer and improving outcomes.
Symptoms of Cancer:
Recognizing the diverse symptoms of cancer is vital for early detection and prompt intervention. While specific signs may vary depending on the type and stage of cancer, the following common symptoms warrant attention:
- Unexplained Weight Loss: A significant and unexplained decrease in body weight, often accompanied by a loss of appetite, could indicate the presence of certain cancers.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Persistent and unexplained exhaustion or weakness may be indicative of cancer, as the disease can impact the body’s energy levels.
- Persistent Pain: Chronic or recurring pain that does not have an apparent cause or does not respond to typical treatments should be assessed, as it may be related to cancer.
- Changes in the Skin: The emergence of new moles or skin growths, changes in existing moles, or alterations in the color, size, or shape of skin lesions may be early signs of skin cancer.
- Persistent Cough or Hoarseness: A persistent cough, particularly if accompanied by blood, and long-lasting hoarseness can indicate underlying respiratory or throat cancer.
- Abnormal Bleeding or Discharge: Unusual bleeding, such as rectal bleeding, blood in urine or stool, or abnormal vaginal bleeding, should be evaluated as it could be associated with various cancers.
- Changes in Bowel or Bladder Habits: Sudden changes in bowel movements, persistent diarrhea or constipation, or frequent urination can be indicative of colorectal, bladder, or prostate cancer.
- Difficulty Swallowing or Persistent Indigestion: Difficulty swallowing, persistent heartburn, or ongoing indigestion may signify gastrointestinal or esophageal cancer.
Causes of Cancer:
Cancer development is multifaceted, influenced by an intricate interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Understanding the underlying causes is essential for prevention and early intervention. Here are some significant factors associated with an increased risk of developing cancer:
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or using tobacco products is a leading cause of various cancers, including lung, throat, mouth, and bladder cancer. Secondhand smoke exposure is also a concern.
- Genetic Predisposition: Certain individuals inherit genetic mutations that predispose them to specific types of cancer, such as breast, ovarian, or colorectal cancer. Genetic counseling and testing can help identify those at higher risk.
- Exposure to Carcinogens: Prolonged exposure to substances like asbestos, benzene, radon, or certain chemicals in the workplace or environment can elevate the risk of cancer.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle: Poor dietary choices, lack of physical activity, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity are lifestyle factors that contribute to an increased risk of developing certain types of cancer.
- Sun Exposure: Overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds can lead to skin cancer, including the potentially deadly melanoma.
Effective Treatments for Cancer:
Medical advancements have revolutionized cancer treatment, offering a range of effective options. Treatment selection depends on factors such as cancer type, stage, and individual health. Here are some commonly used treatments:
- Surgery: Surgical interventions aim to remove cancerous tumors or tissues from the body, either partially or completely. It can be curative or used to alleviate symptoms.
- Radiation Therapy: This treatment employs high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors. It can be administered externally or internally, based on cancer type and location.
- Chemotherapy: Anti-cancer drugs are used to destroy cancer cells or impede their growth. Chemotherapy can be delivered orally, intravenously, or through injections, and may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
- Immunotherapy: This innovative approach harnesses the body’s immune system to identify and attack cancer cells specifically. It includes monoclonal antibodies, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and cancer vaccines.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted drugs focus on specific molecular alterations in cancer cells, disrupting their growth or promoting cell death. This approach minimizes damage to healthy cells.
- Hormone Therapy: Certain cancers, such as breast and prostate cancer, may rely on hormones for growth. Hormone therapy aims to block or interfere with hormone activity to impede cancer progression.
Also read ⬇️

